Mastoidectomy
Restore Ear Health, Prevent Serious Infections
Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that clears infections from the mastoid bone behind the ear. It’s performed to treat chronic ear infections and prevent complications.
Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that clears infections from the mastoid bone behind the ear. It’s performed to treat chronic ear infections and prevent complications.
- Home
- Service
- Mastoidectomy
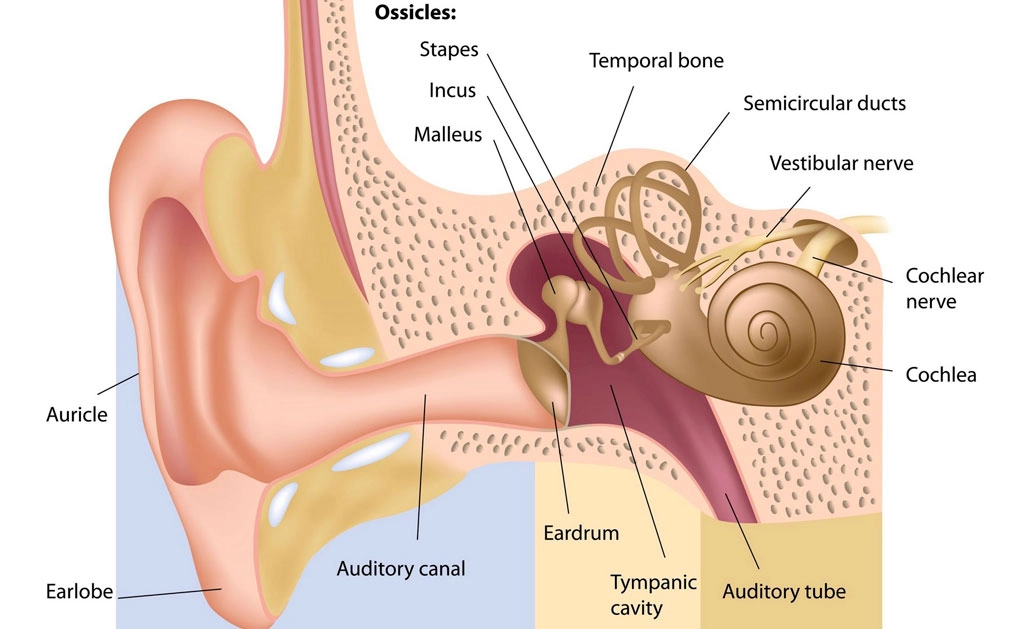
Description
Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove infected air cells from the mastoid bone, located just behind the ear. This condition usually results from chronic otitis media that doesn’t respond to medication alone. If left untreated, it may spread to nearby structures causing hearing loss, vertigo, or even brain abscesses.
There are different types of mastoidectomy — simple, modified radical, and radical — chosen based on the extent of the infection. It is often done using a microscope and high-precision surgical instruments, ensuring safety and accuracy.
There are different types of mastoidectomy — simple, modified radical, and radical — chosen based on the extent of the infection. It is often done using a microscope and high-precision surgical instruments, ensuring safety and accuracy.
Conditions Treated
- Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM)
- Mastoiditis
- Cholesteatoma
- Abscess behind the ear
- Recurrent ear discharge not responding to medication
Tests and Treatments Offered
- High-resolution CT scan of the temporal bone
- Audiometry (hearing test)
- Microscopic ear examination
- Medical therapy before surgery (antibiotics, ear drops)
- Surgical mastoidectomy using advanced ENT tools
Special Offer on Mastoidectomy
Actual Price
₹60,000
₹50,000/- Only
Estimated Stay: 1 Day
Book Appointment
How it works
Procedure and Process Treatment
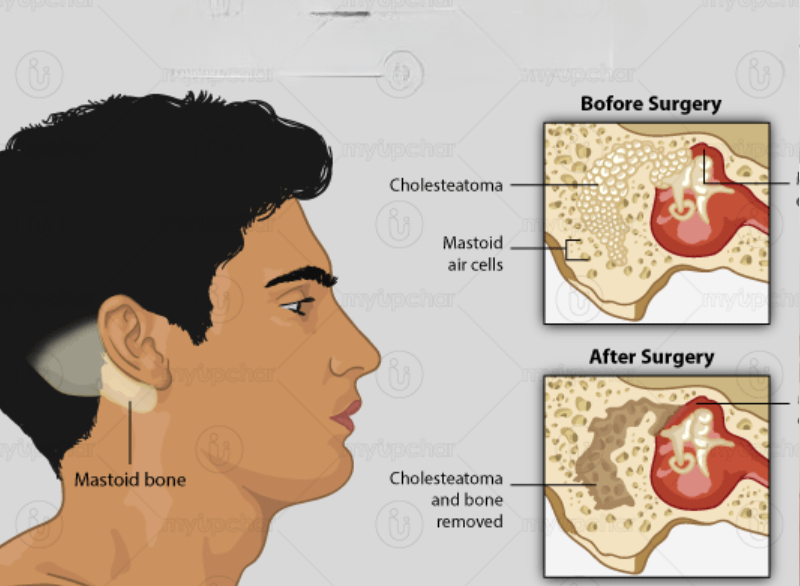
Diagnosis and Imaging
A thorough ENT evaluation and CT scan help confirm mastoid bone infection and decide on the type of surgery required.
Preoperative Preparation
The area is disinfected, and the patient is prepared under general anesthesia. Consent and hearing evaluation are completed.
Surgical Removal
A small incision is made behind the ear, and infected bone is carefully drilled and removed using a surgical microscope.
Recovery and Care
The wound is closed, and the patient is monitored. Antibiotics and ear care instructions are provided for a safe recovery.
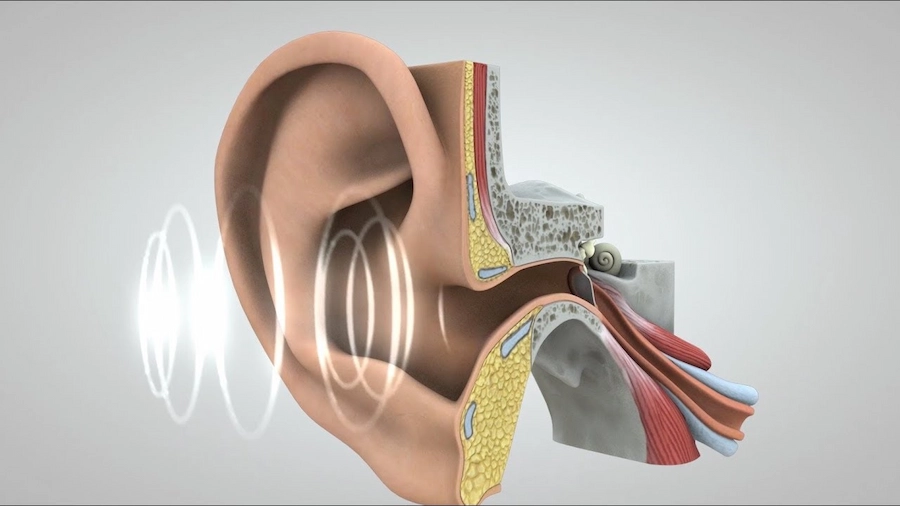
Clear the Path to Better Hearing
Lowcost Surgicals ensures safe, effective mastoidectomy procedures using precise techniques and modern ENT tools. Reclaim your hearing, reduce infection risks, and improve your quality of life — all at affordable care standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
Before undergoing mastoidectomy, patients commonly ask about its safety, results, and aftercare. Here are key clarifications:
It’s considered moderately invasive but is commonly performed and generally safe with modern techniques.
Most patients recover within 1–2 weeks. Some may have mild dizziness or drainage, which resolves with care.
The surgery aims to preserve hearing. Any loss usually results from pre-existing infection, not the surgery itself.


